This article describes how to change a ggplot point shapes.
You will learn how to:
- Change ggplot point shape values. In ggplot, point shapes can be specified in the function
geom_point(). Key arguments include:shape: numeric values aspchfor setting plotting points shapes.size: numeric valuescexfor changing points sizecolor: color name or code for points.
- Modify ggplot point shapes and colors by groups. In this case, you can set manually point shapes and colors. key ggplot2 functions:
scale_shape_manual()andscale_color_manual() - Use special point shapes, including pch 21 and pch 24. The interesting feature of these point symbols is that you can change their background fill color and, their border line type and color.
Contents:
Key R functions
geom_point(aes(x, y), data = NULL, shape = 19, color = "black", size = 1): ggplot2 function to create a scatter plot.scale_shape_manual(),scale_color_manual()andscale_size_manual(): ggplot2 functions to set manually point shape, color and size.
List of point symbols
The most commonly used pch values in R, include:
- shape = 0, square
- shape = 1, circle
- shape = 2, triangle point up
- shape = 3, plus
- shape = 4, cross
- shape = 5, diamond
- shape = 6, triangle point down
- shape = 7, square cross
- shape = 8, star
- shape = 9, diamond plus
- shape = 10, circle plus
- shape = 11, triangles up and down
- shape = 12, square plus
- shape = 13, circle cross
- shape = 14, square and triangle down
- shape = 15, filled square
- shape = 16, filled circle
- shape = 17, filled triangle point-up
- shape = 18, filled diamond
- shape = 19, solid circle
- shape = 20, bullet (smaller circle)
- shape = 21, filled circle blue
- shape = 22, filled square blue
- shape = 23, filled diamond blue
- shape = 24, filled triangle point-up blue
- shape = 25, filled triangle point down blue
The function below illustrates the different point shape values. First install the ggpubr package (install.packages("ggpubr")), and then type this:
ggpubr::show_point_shapes()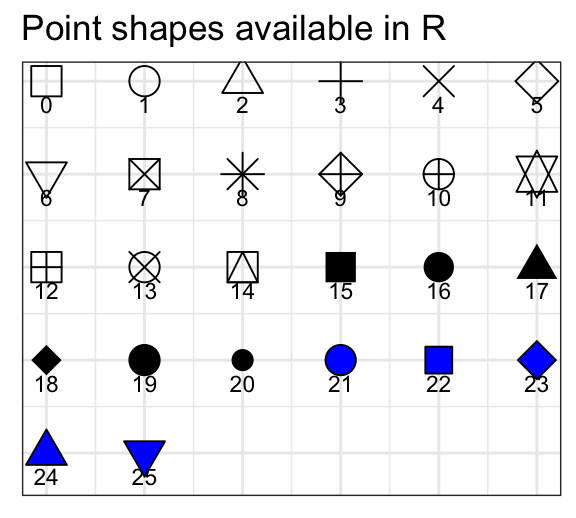
Note that,
- Other different characters symbols can be used to specify the shape argument, including “+”, “*“,”-“,”.“,”#, “%”, “o”.
- shape options from 21 to 25 are open symbols that can be filled by a color.
Demo dataset
We’ll use the R built-in datasets: iris.
head(iris, 3)## Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
## 1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
## 2 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa
## 3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosaBasic scatter plots
Create a scatter plot and change points shape, color and size:
library(ggplot2)
# Change shape, color and size
ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point(shape = 18, color = "#FC4E07", size = 3)+
theme_minimal()
# Change background fill and line color
ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point(shape = 21, fill = "lightgray",
color = "black", size = 3)+
theme_minimal()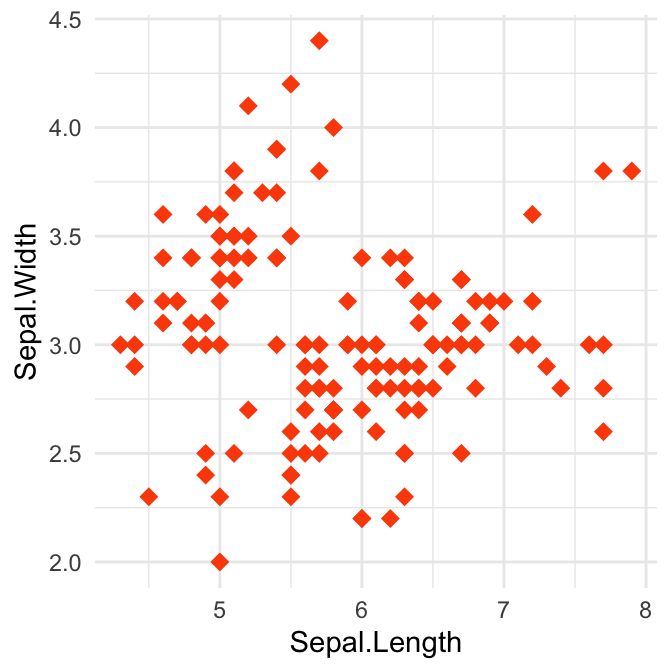
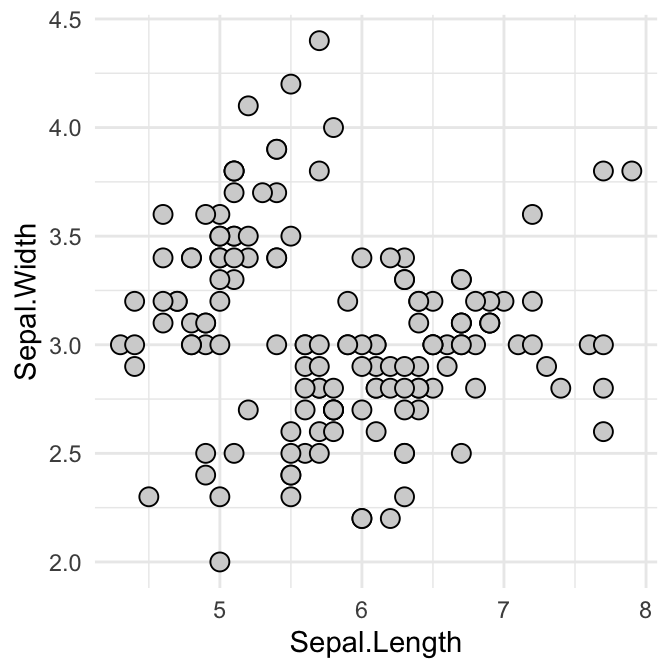
Recall that, the argument fill can be used only for the point shapes 21 to 25.
Scatter plot with multiple groups
It’s also possible to change point shapes and colors by groups. In this case, ggplot2 will use automatically a default color palette and point shapes. You can change manually the appearance of points using the following functions:
scale_shape_manual(): to change manually point shapesscale_color_manual(): to change manually point colorsscale_size_manual(): to change manually the size of points
# Change point shapes and colors by groups
ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point(aes(shape = Species, color = Species), size = 3) +
scale_shape_manual(values = c(5, 16, 17)) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800", "#FC4E07"))+
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "top")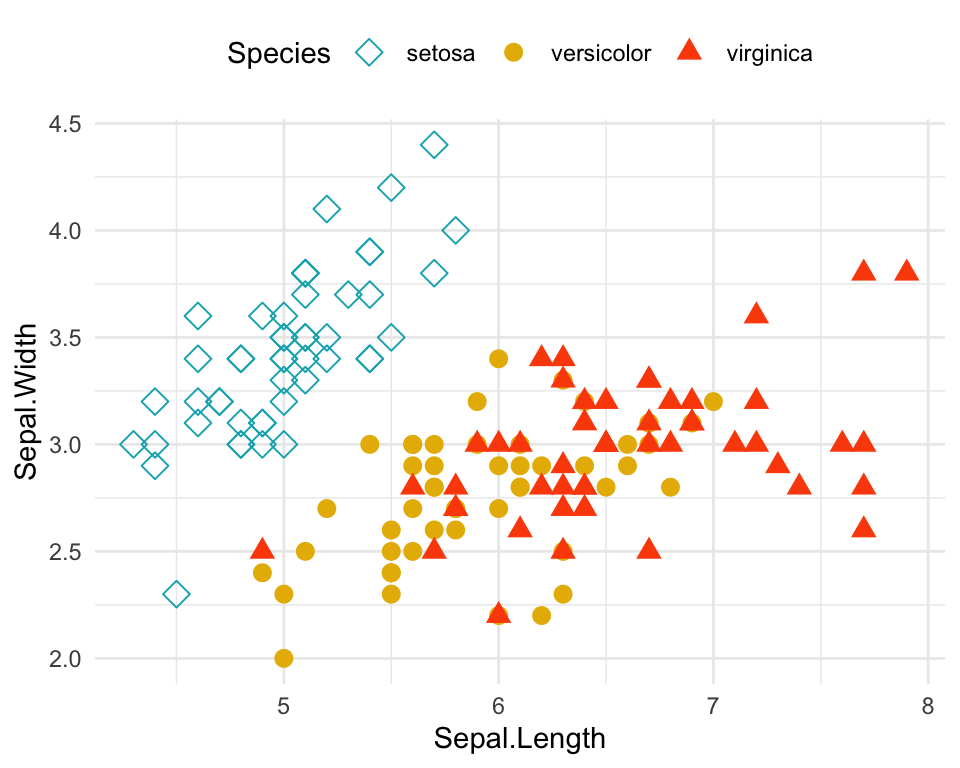
Conclusion
This article describes how to change ggplot point shapes.
- Display the different point symbols in R:
ggpubr::show_point_shapes()- Change point shapes in ggplot2. Use shape, size and color in
geom_point():
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(iris, aes(Sepal.Length, Sepal.Width)) +
geom_point(shape = 18, color = "#FC4E07", size = 3)+
theme_minimal()Recommended for you
This section contains best data science and self-development resources to help you on your path.
Books - Data Science
Our Books
- Practical Guide to Cluster Analysis in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Practical Guide To Principal Component Methods in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Machine Learning Essentials: Practical Guide in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- R Graphics Essentials for Great Data Visualization by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- GGPlot2 Essentials for Great Data Visualization in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Network Analysis and Visualization in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Practical Statistics in R for Comparing Groups: Numerical Variables by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Inter-Rater Reliability Essentials: Practical Guide in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
Others
- R for Data Science: Import, Tidy, Transform, Visualize, and Model Data by Hadley Wickham & Garrett Grolemund
- Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems by Aurelien Géron
- Practical Statistics for Data Scientists: 50 Essential Concepts by Peter Bruce & Andrew Bruce
- Hands-On Programming with R: Write Your Own Functions And Simulations by Garrett Grolemund & Hadley Wickham
- An Introduction to Statistical Learning: with Applications in R by Gareth James et al.
- Deep Learning with R by François Chollet & J.J. Allaire
- Deep Learning with Python by François Chollet
Version:
 Français
Français







I would like to use a hexagon point!! How I do?
Thanks!!