A histogram plot is an alternative to Density plot for visualizing the distribution of a continuous variable. This chart represents the distribution of a continuous variable by dividing into bins and counting the number of observations in each bin.
This article describes how to create Histogram plots using the ggplot2 R package.
Contents:
Related Book
GGPlot2 Essentials for Great Data Visualization in RKey R functions
- Key function:
geom_histgram()(for density plots). - Key arguments to customize the plots:
color, size, linetype: change the line color, size and type, respectivelyfill: change the areas fill color (for bar plots, histograms and density plots)alpha: create a semi-transparent color.
Data preparation
Create some data (wdata) containing the weights by sex (M for male; F for female):
set.seed(1234)
wdata = data.frame(
sex = factor(rep(c("F", "M"), each=200)),
weight = c(rnorm(200, 55), rnorm(200, 58))
)
head(wdata, 4)## sex weight
## 1 F 53.8
## 2 F 55.3
## 3 F 56.1
## 4 F 52.7Compute the mean weight by sex using the dplyr package. First, the data is grouped by sex and then summarized by computing the mean weight by groups. The operator %>% is used to combine multiple operations:
library("dplyr")
mu <- wdata %>%
group_by(sex) %>%
summarise(grp.mean = mean(weight))
mu## # A tibble: 2 x 2
## sex grp.mean
## <fct> <dbl>
## 1 F 54.9
## 2 M 58.1Loading required R package
Load the ggplot2 package and set the default theme to theme_classic() with the legend at the top of the plot:
library(ggplot2)
theme_set(
theme_classic() +
theme(legend.position = "top")
)Basic histogram plots
We start by creating a plot, named a, that we’ll finish in the next section by adding a layer using the function geom_histogram().
a <- ggplot(wdata, aes(x = weight))The following R code creates some basic density plots with a vertical line corresponding to the mean value of the weight variable (geom_vline()):
# Basic density plots
a + geom_histogram(bins = 30, color = "black", fill = "gray") +
geom_vline(aes(xintercept = mean(weight)),
linetype = "dashed", size = 0.6)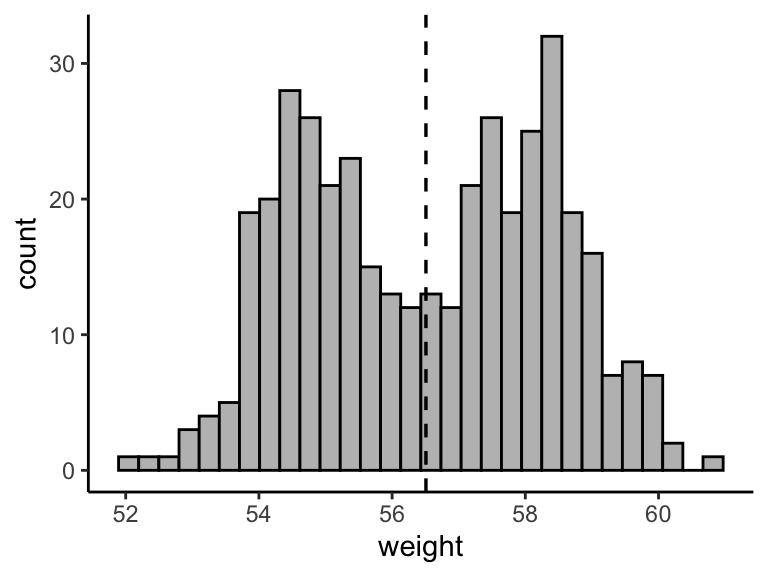
Note that, by default:
- By default,
geom_histogram()uses 30 bins - this might not be good default. You can change the number of bins (e.g.: bins = 50) or the bin width (e.g.: binwidth = 0.5) - The y axis corresponds to the count of weight values. If you want to change the plot in order to have the density on y axis, specify the argument
y = ..density..inaes().
Change color by groups
The following R code will change the histogram plot line and fill color by groups. The functions scale_color_manual() and scale_fill_manual() are used to specify custom colors for each group.
We’ll proceed as follow:
- Change areas fill and add line color by groups (sex)
- Add vertical mean lines using
geom_vline(). Data:mu, which contains the mean values of weights by sex (computed in the previous section). - Change color manually:
- use
scale_color_manual()orscale_colour_manual()for changing line color - use
scale_fill_manual()for changing area fill colors.
- use
- Adjust the position of histogram bars by using the argument
position. Allowed values: “identity”, “stack”, “dodge”. Default value is “stack”.
# Change line color by sex
a + geom_histogram(aes(color = sex), fill = "white",
position = "identity") +
scale_color_manual(values = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800"))
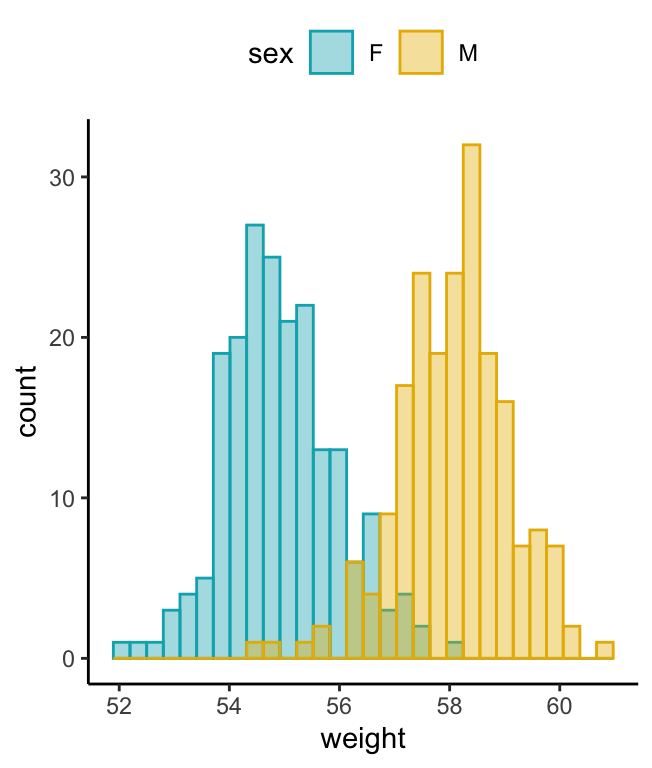
# change fill and outline color manually
a + geom_histogram(aes(color = sex, fill = sex),
alpha = 0.4, position = "identity") +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800")) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800"))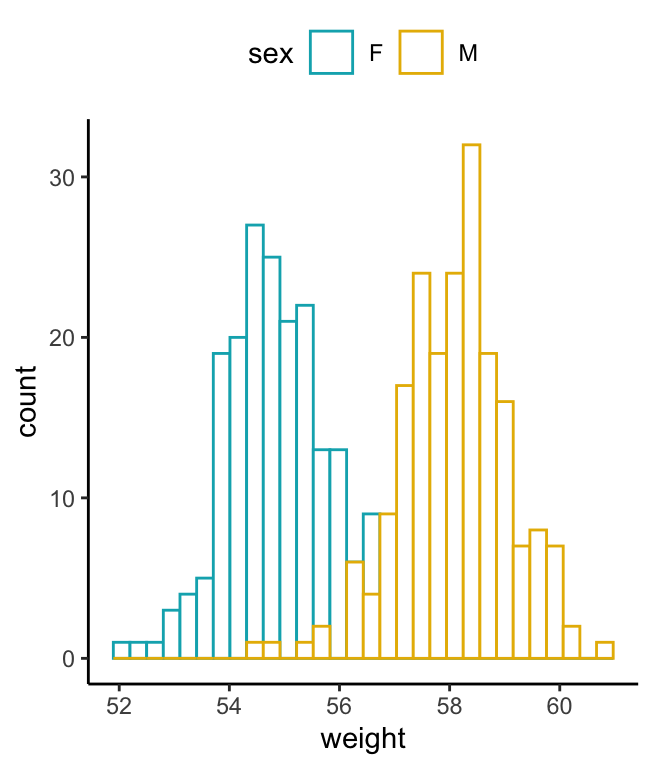
Combine histogram and density plots
- Plot histogram with density values on y-axis (instead of count values).
- Add density plot with transparent density plot
# Histogram with density plot
a + geom_histogram(aes(y = stat(density)),
colour="black", fill="white") +
geom_density(alpha = 0.2, fill = "#FF6666")
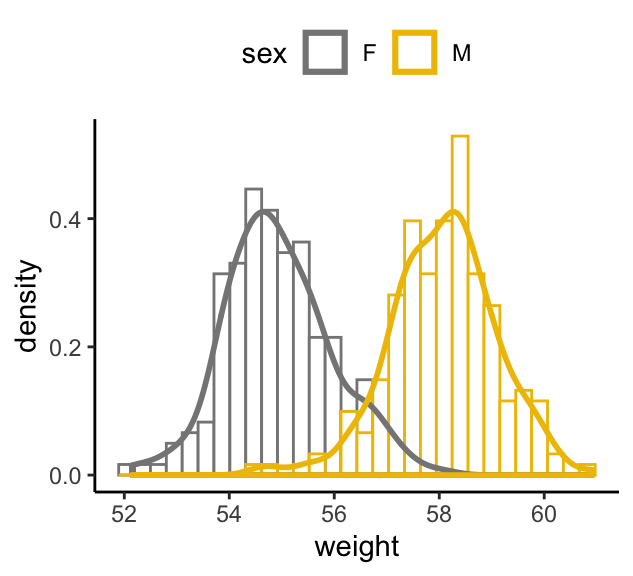
# Color by groups
a + geom_histogram(aes(y = stat(density), color = sex),
fill = "white",position = "identity")+
geom_density(aes(color = sex), size = 1) +
scale_color_manual(values = c("#868686FF", "#EFC000FF"))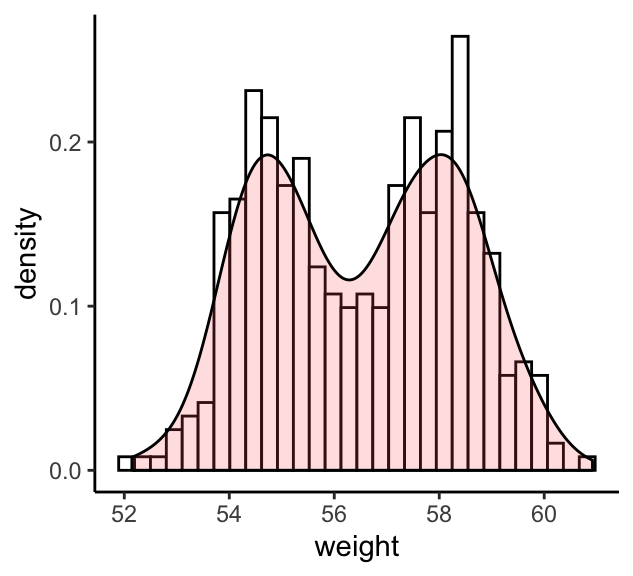
Conclusion
This article describes how to create histogram plots using the ggplot2 package.
Recommended for you
This section contains best data science and self-development resources to help you on your path.
Books - Data Science
Our Books
- Practical Guide to Cluster Analysis in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Practical Guide To Principal Component Methods in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Machine Learning Essentials: Practical Guide in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- R Graphics Essentials for Great Data Visualization by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- GGPlot2 Essentials for Great Data Visualization in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Network Analysis and Visualization in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Practical Statistics in R for Comparing Groups: Numerical Variables by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Inter-Rater Reliability Essentials: Practical Guide in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
Others
- R for Data Science: Import, Tidy, Transform, Visualize, and Model Data by Hadley Wickham & Garrett Grolemund
- Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems by Aurelien Géron
- Practical Statistics for Data Scientists: 50 Essential Concepts by Peter Bruce & Andrew Bruce
- Hands-On Programming with R: Write Your Own Functions And Simulations by Garrett Grolemund & Hadley Wickham
- An Introduction to Statistical Learning: with Applications in R by Gareth James et al.
- Deep Learning with R by François Chollet & J.J. Allaire
- Deep Learning with Python by François Chollet
Version:
 Français
Français



No Comments